Easy Management of billing, payments & Inventory
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems refer to the software packages that integrate all the data and the related processes of an organization. Designed to facilitate the optimization of internal business processes across an enterprise, ERP packages have become a competitive tool for large retail organizations.
An ERP software uses a single database that allows different departments to communicate with each other. ERP systems comprise function-specific features that are designed to interact with other modules such as Order Entry, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Purchasing, etc. Retail ERP software packages have an enterprise-wide reach that offer cross-functional capabilities to the organization.
Main components of Retail ERP System
A cloud-based ERP system includes components to ensure that every business area within the organization relies on a single source, allowing staff to make better decisions faster. The main components of a retail ERP system includes the following:
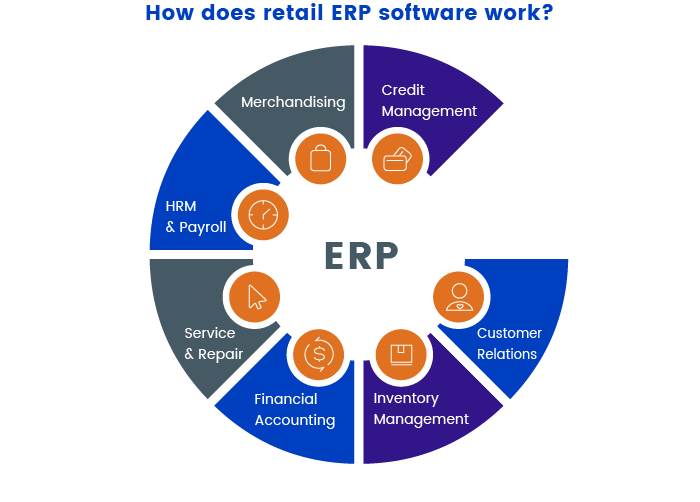
Retail Planning – ERP for retail allows retailers to undertake planning activities as per the need of the situation. It focuses on the different strategies to be employed in order to help a retail store increase sales turnover.
Store Operations – ERP for retail helps streamline operations related to the store management function. The store operations are central to retail chains since market basket analysis, merchandising, inventory management, workforce management and much more is part of this.
Inventory Management – This component enables retailers of all types and sizes to effectively manage the inventory levels and track goods. Inventory Management is the process of overseeing the constant flow of units into and out of an existing inventory. Inventory often accounts for the highest proportion of the working capital as raw material, WIP and finished goods.
Supply Chain Management – ERP for retail manages the end-to-end supply chain for retailers. Shipping of products or materials dealing with potentially massive amounts of data scattered throughout the world, ERP systems can help ensure information stays interconnected and can be easily accessed by all relevant stakeholders.
Demand Forecasting – Tracking past trends and forecasting future demands is easier and higher on accuracy with ERP for retail. Maintain customer satisfaction, maximize sales and reduce inventory carrying costs with ERP for retail.
Vendor Management – Capture vendor details, lead time, performance and other vendor details. Perform comparison between vendors and choose preferred vendor with ERP for retail.
Customer Management – Customer management becomes easy with the automated processes for capturing customer data, preferences and activities with ERP for retail. Track and increase customer lifetime value with ERP for retail. Get new customers, identify your best customers, keep them engaged and build your brand.
Finance Management – Retailers can manage their accounting easily with ERP for retail as it provides a comprehensive set of tools required to manage all the financial aspects of your business, while maintaining a high level of regulatory compliance.
Database Integration – A comprehensive ERP for retail helps in process management and provides access to real-time reports. ERP makes the required data available to provide insights into the financial health of a retail business. Moreover, this component of retail ERP systems is used for generating specific compliance reports.